Note: This publication is currently undergoing major revisions. The current publication will be replaced with a new publication based on stakeholder requirements and scientific advances. We expect to begin sharing details on this soon. If you have input on content, format, or publication frequency at any time, please contact us at cbrfc.webmasters@noaa.gov.Upper Colorado Water Supply Outlook, February 1, 2011Upper Colorado Water Supply Outlook, February 1, 2011
Contents
Upper Colorado Summary
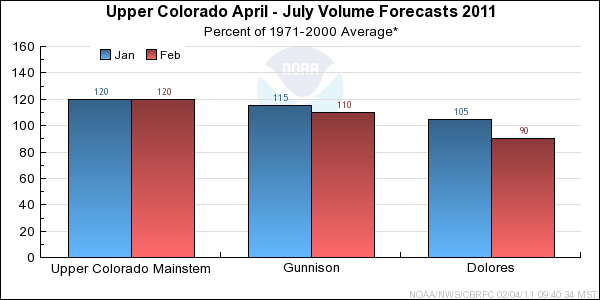
*Median of forecasts within each basin.
Upper Colorado Mainstem Basin Conditions
The following conditions influenced this month's forecasts:
Precipitation:
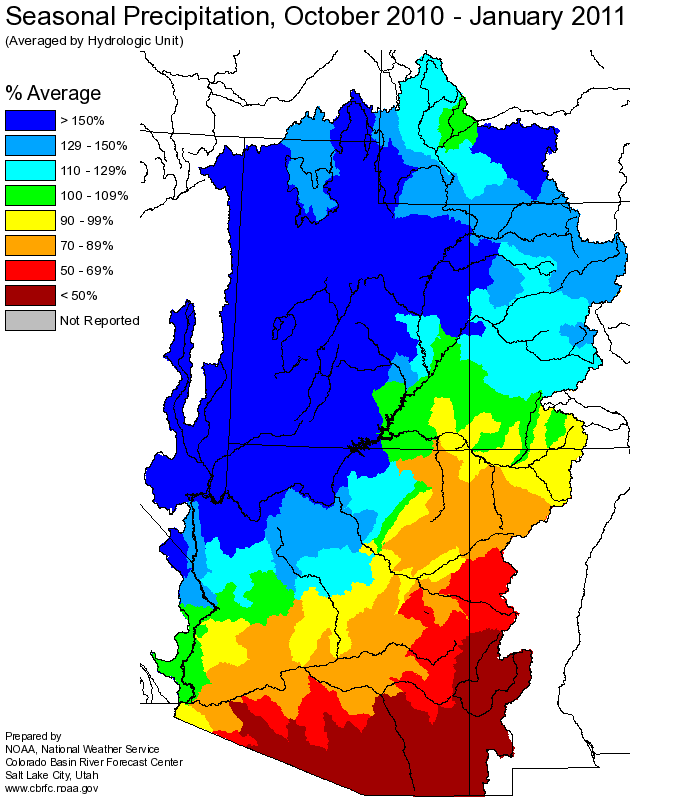
Seasonal October through January
precipitation
was near 135 percent of average in the Upper Colorado mainstem basin.
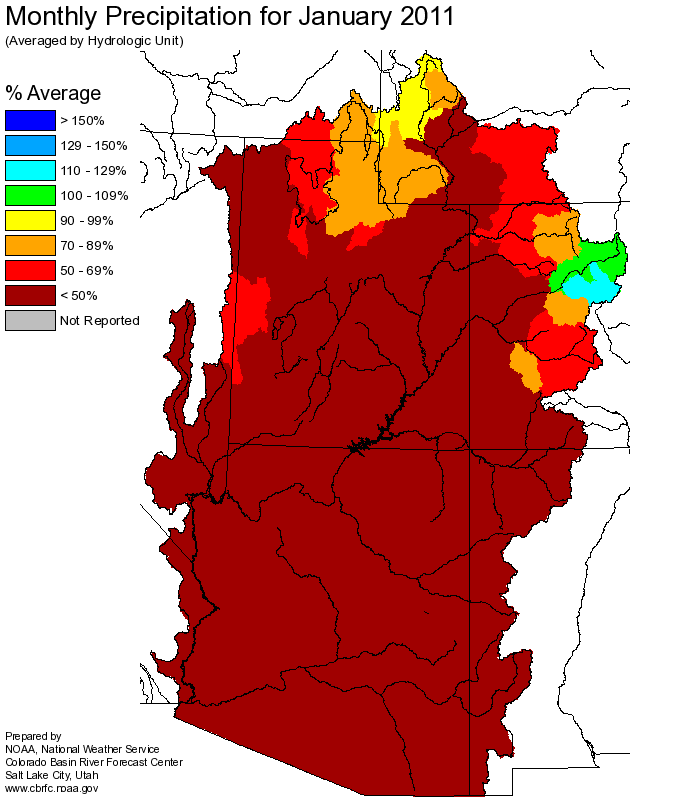
January
precipitation was near 85 percent of average in the basin
as a whole, however upper portions of the basin, such as the Blue and Eagle river basins
and the mainstem headwaters, received near to above average precipitation.
Snow:
February 1st snow water equivalent was near 130 percent of average in the basin
as a whole; this is 75% of the seasonal peak.
--- Upper Colorado basin
snow
water equivalent plot
Streamflow:
February streamflow was near 95 percent of average.
Soil Moisture:
Modeled
soil
moisture states were near to above average heading into the winter.
Climate Forecasts:
Climate forecasts were not a factor because there is not a strong correlation
between La Nina conditions and winter precipitation in the Upper Colorado mainstem basin.
Forecast Summary:
January was the first month of this water year with below average precipitation in the
Upper Colorado mainstem basin; monthly precipitation had been above to much above average
each month of the water year prior to January. As of February 1st the percent of average
of both the seasonal precipitation and snow water equivalent are lower than they were at
the start of last month, but still much above average in the basin as a whole.
Most forecast volumes are the same as last month. Decreases
at the Colorado River near Cisco and Lake Powell inflow were due to changes in other
contributing basins. Current April through July streamflow volume
forecasts
range between 113 and 139 percent of average with a median value of 120 percent.

* Percent usable capacity, not percent average contents.
Click for multi-month Graph.
Gunnison Basin Conditions
The following conditions influenced this month's forecasts:
Precipitation:
Seasonal October through January
precipitation was 125 percent of average
in the Gunnison basin. January
precipitation was 55 percent of average.
Snow:
February 1st snow water equivalent was near 130 percent of average in the Gunnison basin; this is 75% of the seasonal peak.
--- Gunnison basin
snow
water equivalent plot
Streamflow:
January streamflow was 95 percent of average.
Soil Moisture:
Modeled
soil
moisture states were below to near average heading into the winter.
Climate Forecasts:
Climate forecasts were not a factor because there is not a strong correlation
between La Nina conditions and winter precipitation in the Gunnison basin.
Forecast Summary:
January precipitation throughout the Gunnison basin was much below average at 55%. Seasonal precipitation for the Gunnison basin dropped from last month to 125% of average.
February 1st seasonal snow water equivalent for the Gunnison was above average with 130%; whereas the snow water equivalent is 75% of the average seasonal peak.
Since the percent of average for both seasonal snow water equivalent and seasonal precipitation decreased from last month, the current April through July streamflow volume forecasts dropped
in the Gunnison Basin from last month's forecast. Current April through July streamflow volume
forecasts range between 93 and 126 percent of average with a median value of
110 percent.

* Percent usable capacity, not percent average contents.
Click for multi-month Graph.
Dolores Basin Conditions
The following conditions influenced this month's forecasts:
Precipitation:
Seasonal October through January
precipitation was 110 percent of average
in the entire Dolores basin. January
precipitation was just 25 percent of average.
Snow:
February 1st snow water equivalent was 100 percent of average in the Dolores basin as a whole; this is 60% of the seasonal peak.
--- Dolores basin
snow
water equivalent plot
Streamflow:
January streamflow was 95 percent of average.
Soil Moisture:
Modeled
soil
moisture states were average to slightly below average heading into the winter.
Climate Forecasts:
The correlation of La Nina and April through July water volumes in the Dolores basin is small that
it did not influence the forecast process.
Forecast Summary:
January precipitation throughout the Dolores basin was much below average at 25%. Seasonal precipitation for the Dolores basin dropped from last month to 110% of average.
February 1st seasonal snow water equivalent for the Dolores was average with 110%; whereas the snow water equivalent is 60% of the average seasonal peak.
Since the percent of average for both seasonal snow water equivalent and seasonal precipitation decreased from last month, the current April through July streamflow volume forecasts
dropped in the Dolores Basin from last month's forecast. Current April through July streamflow volume
forecasts range between
87 and 93 percent of average, with a median value of 90 percent.
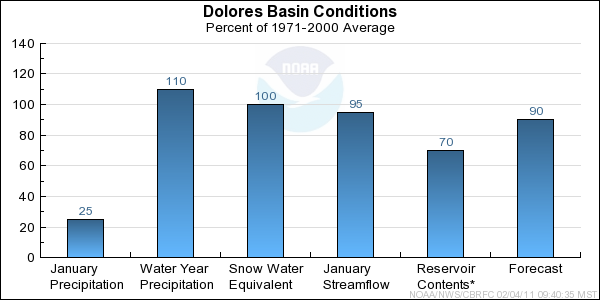
* Percent usable capacity, not percent average contents.
Click for multi-month Graph.
Differences between the full period forecasts and the residual forecasts may not exactly equal the actual observed volumes due to rounding conventions (see Definitions section).
Reservoir Monthly Inflow Forecasts
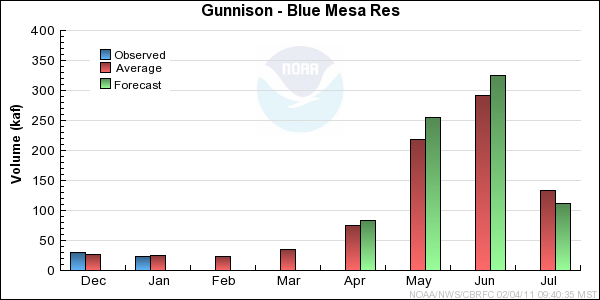
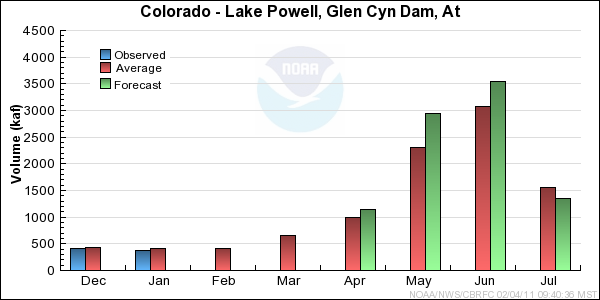
Monthly Streamflows
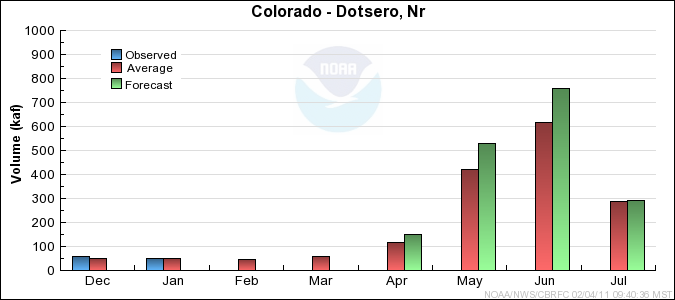
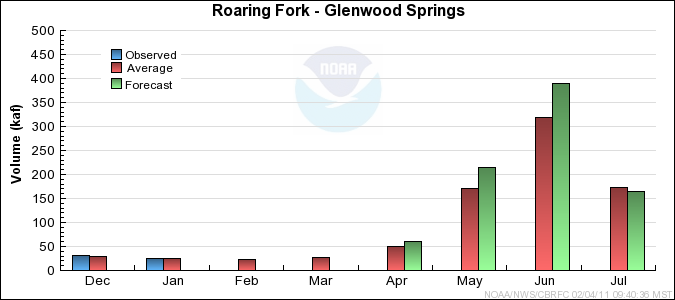
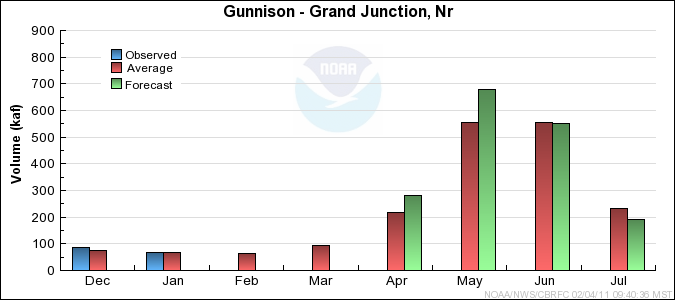
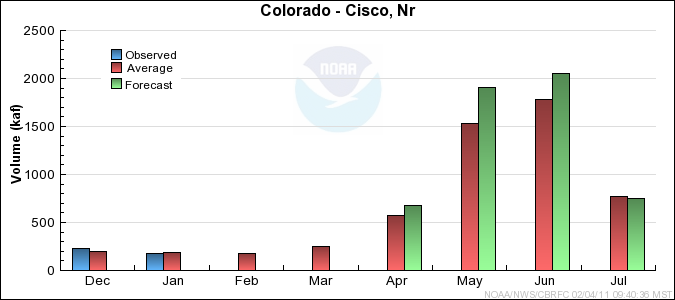
Precipitation Maps
Hydrologist: Brenda Alcorn, Tracy Cox













